| |
Stochastic Process
|
A random variable, {X(t)}, where
t is a time
index that takes values from a given set T.
T may be discrete or continuous. X(t)
is a scalar that may take discrete or continuous values.
We consider here only finite-discrete stochastic processes. |
|
|
Time
|
The parameter of a stochastic process.
|
| |
State
|
A vector that describes attributes of a system at any
point in time. The state vector has m components.
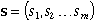
X(t) describes some feature
of the state.
|
| |
State Space
|
Collection of all possible states. |
| |
Activity
|
An activity begins at some point in time, has a duration
and culminates in an event. Generally the duration of
the activity is a random variable with a known probability
distribution. |
| |
Event
|
The culmination of an activity. The event has the potential
to change the state of the process. |
| |
Calendar
|
The set of events that can occur in a specified state,
Y(s). |
| |
Next Event
|
While in some state when one or more events can occur,
the one that occurs next is called the next event. Measured
from the current time, the time of the next event is:
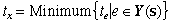
The next event is the value of x
that obtains the minimum. When the durations of events
are random variables both the next event and the time
of the next event are random variables.
|
| |
Transition
|
A function that determines the next state, s',
based on the current state, s, and the event, x. The number of elements
of the transition function is the same as the number of
elements in the state vector.
s'
= T(s,x).
|
| |
State-transition network
|
A graphical representation of the states, represented
by nodes, and events, represented by arcs. A transition
is shown as a directed arc going from one node to another. |
| |
Markovian Property
|
Given that the current state is known, the conditional
probability of the next state is independent of the states
prior to the current state. |
| |
Discrete-Time Markov Chain
|
A stochastic process that satisfies the Markovian property
and has a discrete time parameter. Sometimes such a process
is call simply Markov Chain. |
| |
Continuous-Time Markov Chain
|
A stochastic process that satisfies the Markovian property
and has a continuous time parameter. Sometimes such a
process is call a Markov Process. |
| |
|
|

