|
|
 |
Linear/Integer
Programming Solver |
 |
The LP/IP Solver add-in provides an algorithm that solves Linear
Programming problems. It can be used instead of the Excel solver
for the linear programming models created by the Mathematical
Programming add-in. It also works when some or all of the variables
are required to be integer. When it is installed, a new item
appears on the OR_MM menu, LP/IP Solver. Subroutines provided
by the algorithm are called when the user clicks on the Solve
button on the linear, integer, or mixed integer model sheets.
The LP/IP Solver menu item will show a dialog only when a mathematical
programming model constructed with the Math Programming add-in
is present on the active worksheet. Otherwise the message below
indicates that it is not available.
"This is not a valid worksheet for the
LP/IP Solver"
|
| |
-
|
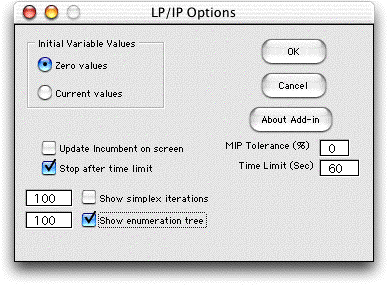
When a valid worksheet is active, choosing the LP/IP Solver
menu item presents the dialog below. These options only affect
the Jensen LP/IP Solver, and do not affect the Excel Solver. |
| |
Solution Display Options
These options create a separate worksheet for algorithm details
that shows iteration information from the solution algorithms.
The reports are useful for the student who is learning about
the solution methods used.
Simplex Iterations
This option creates a new worksheet with the suffix Details.
Information about the iterations of the primal simplex are
printed on this worksheet. The number field to the left on
the dialog holds the number of iterations to be displayed.
Since some problems may require thousands of iterations, this
number should be set to a reasonable value or the memory requirement
for Excel will be excessive.
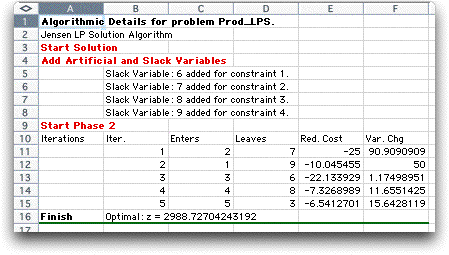
The figure below shows the detail worksheet for the Production
problem described earlier. The display shows the slack variables
added for the four constraints. No artificial variables are
required. Five simplex iterations are required to find a solution.
The display shows details about the iterations.
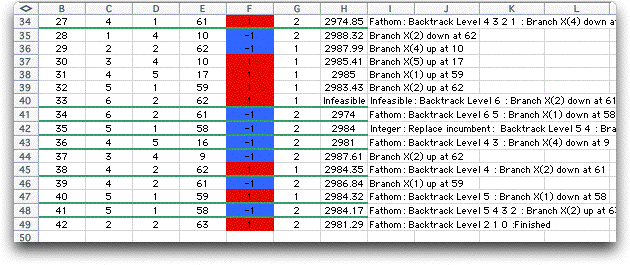
Enumeration Tree
When the production variables are required to be integer,
the LP_IP add-in can be used to show the details of the enumeration
process. Using the LP/IP Solver dialog we click the Show
Enumeration Tree checkbox. The number field to the left
on the dialog is the number of enumeration tree vertices to
be displayed.
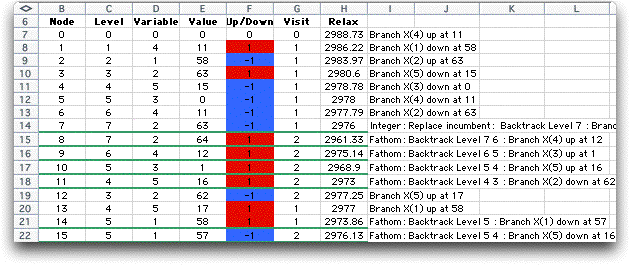
While the problem is solved a record is kept of
the enumeration process and displayed on the Details
worksheet. The example requires an enumeration tree with 42
vertices.
Clicking both display checkboxes will show both
the enumeration tree and subsequent steps of the simplex the
simplex method used by the bounding procedure.
|
| |
Algorithm Control Options
Initial Variable Values
Two different starting strategies are available. The first
option starts with all variables values equal to 0. The second
strategy gathers the initial variable values from the values
shown on the worksheet.. The algorithm starts with these values.
This advanced start option reduces the number of iterations
required when only slight modifications are made to the model.
MIP Tolerance
When solving all integer or mixed integer programming problems,
vertices of the enumeration tree are fathomed when the relaxed
solution objective is less than (for a maximization problem)
than the incumbent solution. This tolerance makes the fathoming
test a little easier by fathoming the vertex if its relaxed
objective is within x% of the incumbent solution, where x
is the number entered in this field. The solution may be found
with fewer iterations and less time when this value is greater
than 0. When the tolerance is other than 0, however, there
is no guarantee that the optimum solution is obtained. It
is a guaranteed that the solution is with x% of the optimum.
The Excel Solver has a similar tolerance specified in the
Options dialog of the Solver.
Time Limit
When solving all integer or mixed integer programming problems,
the process may take a long time. The program will stop when
this time limit is reached. The user may give up at this point
or continue the optimization. The Excel Solver has a similar
time limit specified in the Options dialog of the Solver.
Update Incumbent on the Screen
When solving all integer or mixed integer programming problems,
the algorithm may find feasible solutions during the enumeration
process. The feasible solution with the best value is called
the incumbent solution. Although intermediate steps are not
displayed on the model worksheet while the process continues,
when this checkbox is selected, the display will be changed
whenever a new incumbent is discovered.
|
|



