| Function |
Notation
|
Result
|
Q_type(Q_Sample):
Determines the type of queue using Kendall's notation. |
Type =
|
M/M/3
|
Q_L(Q_Sample):
Computes the mean number in the system. |
L=
|
6.011236
|
Q_W(Q_Sample):
Computes the mean number in the system. |
W =
|
1.2022472
|
Q_Lq(Q_Sample):
Computes the mean number in the queue. |
Lq=
|
3.511236
|
Q_Wq(Q_Sample):
Computes the mean time in the queue. |
Wq =
|
0.7022472
|
Q_Ls(Q_Sample):
Computes the mean number in service. |
Ls=
|
2.5
|
Q_Ws(Q_Sample):
Computes the mean time in service. |
Ws =
|
0.5
|
Q_LamB(Q_Sample):
Computes the throughput of the station. |
LamB =
|
5
|
Q_Eff(Q_Sample):
Computes the efficiency of the servers. |
Eff =
|
0.8333333
|
Q_P0(Q_Sample):
Computes the probability of 0 in the system. |
P0 =
|
0.0449438
|
Q_PB(Q_Sample):
Computes the probability that all servers are busy. |
PB =
|
0.7022472
|
Q_PF(Q_Sample):
Computes the probability that the system is full. |
PF =
|
0
|
Q_FNext(k,
Q_Sample):
The FNext function computes the factor to obtain the next probability
in a series of state probabilities. The function must be multiplied
by the previous probability. k is the index of the state computed.
P(1) = P(0)*FNext(1, Queue) |
P(1) =
|
0.1123596
|
Q_Pn(k, Q_Sample):
Computes the probability of n customers in the system. Illustrated
for 11. |
P(11) =
|
0.02722
|
|
Q_PTq(time, Q_Sample):Computes
the cumulative probability distribution of the waiting time
in the queue. An example of this function is shown below.
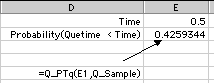
|
PTq(0.5) =
|
0.4259344
|



